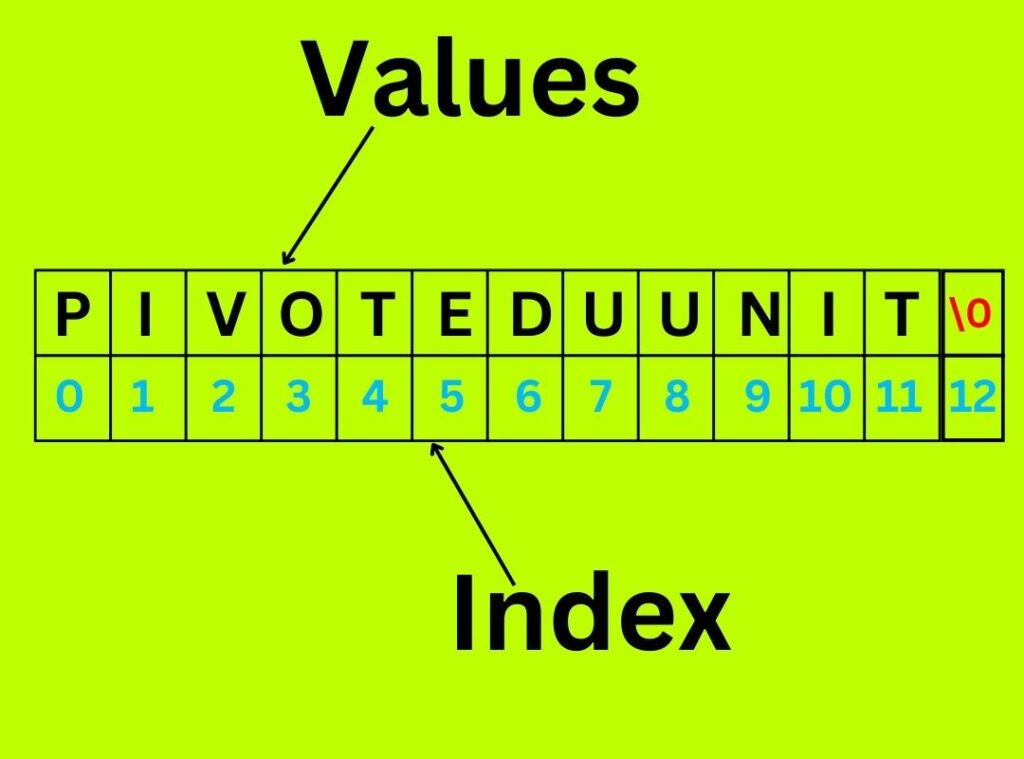
In C programming, a string is essentially an array of characters ending with a null character ('\0'). This null character signifies the end of the string. Strings are used to store and manipulate text, making them a crucial aspect of many programs.
char str[12]={“PIVOTEDUUNIT”}
Here are some question on Strings for better understanding
Write a program in C to input a string and print it.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read a string including spaces
printf("You entered: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
WAP in C to Read & write Strings in C using Printf() and Scanf() functions
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
/* String Declaration*/
char nickname[20];
printf("Enter your Nick name:");
/* Reading String Using Scanf */
scanf("%s", nickname); // Note there is No "&" while Reading String
/*Printing String*/
printf("%s",nickname);
return 0;
}
Read & Write Strings in C using gets() and puts() functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
/* String Declaration*/
char nickname[20];
/* Getting Message to Show Message using puts */
puts("Enter your Nick name:");
/*Input using gets*/
gets(nickname);
puts(nickname);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to find the length of a string without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, count = 0;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string (optional, can be replaced with getchar() loop)
// Iterate through the string until the null terminator is found
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
count++;
}
printf("The length of the string is %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to separate individual characters from a string without using built-in functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string
printf("Individual characters:\n");
// Iterate through the string until the null terminator is found
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
printf("%c ", str[i]); // Print each character with a space
}
printf("\n"); // Add a newline at the end
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to print individual characters of a string in reverse order without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, length;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string
// Find the length of the string (excluding null terminator)
length = 0;
while (str[length] != '\0') {
length++;
}
printf("Characters in reverse order:\n");
// Iterate from the end of the string to the first character
for (i = length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%c ", str[i]); // Print each character with a space
}
printf("\n"); // Add a newline at the end
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to count the total number of words in a string without using built-in functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, word_count = 0;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string
// Consider the first character as a potential word start
if (str[0] != ' ' && str[0] != '\0') {
word_count++;
}
// Iterate through the string
for (i = 1; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
// Check for transition from non-space to space (word boundary)
if (str[i] == ' ' && str[i - 1] != ' ') {
word_count++;
}
}
printf("The number of words in the string is: %d\n", word_count);
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to concat two strings using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char s1[10] = "Hello";
char s2[10] = "World";
strcat(s1,s2);
printf("Output string after concatenation: %s", s1);
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to reverse a string using built-in functions.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char str[20];
printf("Enter string: ");
gets(str);//takes input string from user
printf("String is: %s",str);
printf("\nReverse String is: %s",strrev(str));
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to convert string from upper to lower case using built-in functions.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char str[20];
printf("Enter string: ");
gets(str);//Takes Input string from user
printf("String is: %s",str);
printf("\nLower String is: %s",strlwr(str));
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to convert string from upper to lower case using built-in functions.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char str[20];
printf("Enter string: ");
gets(str);//Takes Input string from user
printf("String is: %s",str);
printf("\nLower String is: %s",strlwr(str));
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to convert string from upper to lower case without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i;
printf("Enter a string in uppercase: ");
fgets(str, sizeof(str), stdin);
// Remove trailing newline from fgets
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0';
// Convert to lowercase
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (str[i] >= 'A' && str[i] <= 'Z') {
str[i] = str[i] + 32; // Add 32 to convert uppercase to lowercase
}
}
printf("String in lowercase: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
WAP in C program to convert string from lower to upper case without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i;
printf("Enter a string in lowercase: ");
fgets(str, sizeof(str), stdin);
// Remove trailing newline from fgets
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0';
// Convert to uppercase
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z') {
str[i] = str[i] - 32; // Subtract 32 to convert lowercase to uppercase
}
}
printf("String in uppercase: %s\n", str);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to count the total number of alphabets, digits and special characters in a string without built-in functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, alphabets = 0, digits = 0, special_chars = 0;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string
// Iterate through the string
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
char ch = str[i];
// Check for alphabets (lowercase and uppercase)
if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z')) {
alphabets++;
} else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
digits++;
} else {
special_chars++;
}
}
printf("Number of alphabets: %d\n", alphabets);
printf("Number of digits: %d\n", digits);
printf("Number of special characters: %d\n", special_chars);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to compare two strings without using string library functions without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str1[100], str2[100];
int i, mismatch = 0;
printf("Enter the first string: ");
fgets(str1, 100, stdin); // Read the first string
printf("Enter the second string: ");
fgets(str2, 100, stdin); // Read the second string
// Compare characters one by one, incrementing a mismatch flag if differences are found
for (i = 0; str1[i] != '\0' || str2[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (str1[i] != str2[i]) {
mismatch = 1;
break; // Exit the loop on the first mismatch
}
}
if (mismatch == 0) {
printf("Strings are equal.\n");
} else {
printf("Strings are not equal.\n");
}
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to copy one string to another string without built-in functions
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str1[100], str2[100];
int i;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str1, 100, stdin); // Read the string (optional, can be replaced with a loop using getchar())
// Iterate through the string and copy characters one by one
i = 0;
while (str1[i] != '\0') {
str2[i] = str1[i];
i++;
}
// Add the null terminator manually to the copied string
str2[i] = '\0';
printf("Copied string: %s\n", str2);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to find the maximum number of characters in a string without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, length = 0;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string (optional, can be replaced with a loop using getchar())
// Iterate through the string until the null terminator is found
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
length++;
}
printf("The maximum number of characters in the string is: %d\n", length);
return 0;
}
Write a C program to sort a string array in ascending order without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int i, length = 0;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string (optional, can be replaced with a loop using getchar())
// Iterate through the string until the null terminator is found
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
length++;
}
printf("The maximum number of characters in the string is: %d\n", length);
return 0;
}
Write a C program to check whether a substring is present in a string without using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char str[100], sub_str[50];
int i, j, found = 0;
printf("Enter the main string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the main string
printf("Enter the substring to search: ");
fgets(sub_str, 50, stdin); // Read the substring
// Remove the newline character (optional)
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0'; // Using strcspn for newline check (optional)
sub_str[strcspn(sub_str, "\n")] = '\0'; // Optional, can be commented out
// Iterate through the main string
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
// Check if the current character matches the first character of the substring
if (str[i] == sub_str[0]) {
// Inner loop to compare substring characters
for (j = 0; sub_str[j] != '\0' && str[i + j] != '\0' && sub_str[j] == str[i + j]; j++) {
// Continue as long as characters match
}
// Check if the inner loop completed without mismatch (substring found)
if (sub_str[j] == '\0') {
found = 1;
break; // Exit the outer loop if substring found
}
}
}
if (found == 1) {
printf("Substring is present in the main string.\n");
} else {
printf("Substring is not present in the main string.\n");
}
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to find the length of a string using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // For strlen
int main() {
char str[100];
int length;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the string (including newline)
length = strlen(str); // Use strlen to get the length (excluding null terminator)
printf("The length of the string is: %d\n", length - 1); // Adjust for newline
return 0;
}
Here’s a C program to check whether a substring is present in a string using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // For strstr
int main() {
char str[100], sub_str[50];
char *result;
printf("Enter the main string: ");
fgets(str, 100, stdin); // Read the main string (including newline)
printf("Enter the substring to search: ");
fgets(sub_str, 50, stdin); // Read the substring (including newline)
// Remove trailing newline (optional)
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0';
sub_str[strcspn(sub_str, "\n")] = '\0';
result = strstr(str, sub_str); // Search for substring in main string
if (result != NULL) {
printf("Substring is present in the main string.\n");
} else {
printf("Substring is not present in the main string.\n");
}
return 0;
}
Write a C program to sort a string array in ascending order using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // For strcmp and qsort
int compareStrings(const void *a, const void *b) {
const char *strA = (const char *)a;
const char *strB = (const char *)b;
return strcmp(strA, strB);
}
int main() {
char str_array[100][50]; // Array to store strings (adjust size as needed)
int num_strings, i;
printf("Enter the number of strings: ");
scanf("%d", &num_strings); // Read the number of strings
printf("Enter %d strings:\n", num_strings);
for (i = 0; i < num_strings; i++) {
scanf("%s", str_array[i]); // Read each string
}
printf("\nStrings before sorting:\n");
for (i = 0; i < num_strings; i++) {
printf("%s\n", str_array[i]);
}
qsort(str_array, num_strings, sizeof(str_array[0]), compareStrings); // Sort the array
printf("\nStrings after sorting:\n");
for (i = 0; i < num_strings; i++) {
printf("%s\n", str_array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to copy one string to another string using built-in functions
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // For strcpy
int main() {
char source[100], destination[100];
printf("Enter a string to copy: ");
fgets(source, 100, stdin); // Read the source string (including newline)
// Remove trailing newline (optional)
source[strcspn(source, "\n")] = '\0';
strcpy(destination, source); // Copy using strcpy
printf("The copied string is: %s\n", destination);
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to compare two strings without using string library functions using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str1[100], str2[100];
printf("Enter the first string: ");
scanf("%s", str1);
printf("Enter the second string: ");
scanf("%s", str2);
int result = strcmp(str1, str2);
if (result == 0)
printf("Both strings are equal.\n");
else if (result < 0)
printf("First string is lexicographically less than second string.\n");
else
printf("First string is lexicographically greater than second string.\n");
return 0;
}
Write a program in C to find the length of a string using built-in functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
int length;
printf("Enter a string: ");
fgets(str, sizeof(str), stdin);
// Remove trailing newline from fgets
str[strcspn(str, "\n")] = '\0';
// Use strlen to get the length (excluding null terminator)
length = strlen(str);
printf("The length of the string is: %d\n", length);
return 0;
}










